
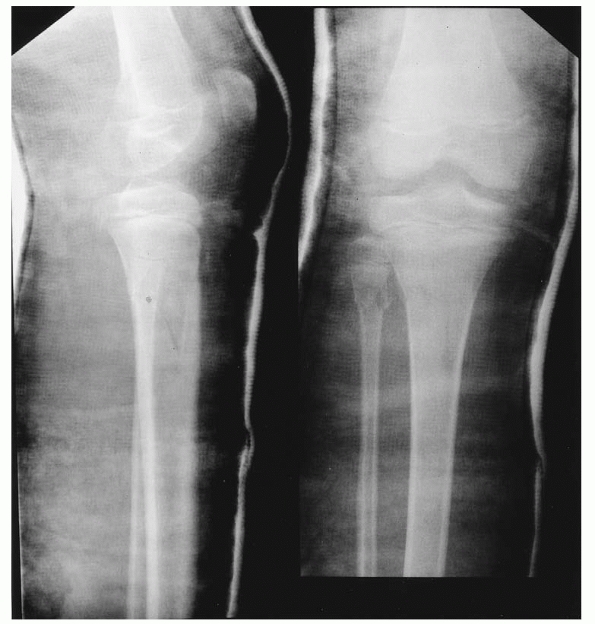
Children usually present limping or refusing to walk. It is caused by a twisting injury while tripping, stumbling, or falling. The initial injury is often not witnessed. Answer Toddler's fracture, also called childhood accidental spiral tibial fracture or CAST fracture, is a fracture unique to ambulatory infants and young children. It usually takes a combination of surgery, rest, and physical therapy to recover from spiral. Diaphyseal tibia fractures in the pediatric population have dynamic treatment strategies that depend on injury pattern, mechanism, patient skeletal maturity and size. The name derived from the shape of the fracture along the diaphysis of a long bone. Toddler fracture is caused by a rotational shearing force in a newly walking child. A spiral fracture is a bone fracture that occurs when a long bone is broken by a twisting force. Spiral fractures typically occur in children, with the tibia being a common site. Whether this is always necessary or whether the outcome is similar without a cast or with a backslabsplint is currently debated. The usual management is immobilisation in a long (above knee) cast for about 3 weeks.

On occasions though the fracture is suspected clinically it is only possible to diagnose it on a delayed (at 10 days) X-ray showing callus formation or on other imaging such as a bone scan. Sometimes the fracture may even be less obvious than this with only a minor cortical irregularity while at other times the spiral nature of the fracture is obvious. Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures (DTMF) are rare fractures among children, and are usually treated by closed methods for 6 to 8 weeks with reported. This is a spiral type fracture of the tibial shaft (in this case visible in both the AP and oblique in the mid to upper third of the tibia). Tibial shaft fractures in children and adolescents. The x-ray demonstrates what is known as a “toddler fracture”. Spiral fracture on the left distal tibia: Spiral tibia fractures can be sometimes seen on anterior and lateral view as a faint dark line (white arrow), which can often be mistaken for a nutritive vessel.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
